You are viewing 1 of your 1 free articles
Preventing crosses
This session is about full-backs and wingers stopping crosses into the penalty area. Most attacks come from out wide, so the ability for defenders to be able to block crosses is essential, particularly in matches when our opponents have strikers who are good headers of the ball. This applies to most teams in our division. At the end of each phase, we reset play, and rotate positions regularly.
| Area | Up to half pitch |
| Equipment | Balls, cones, goals |
| No. of Players | Up to 18 players |
| Session Time |
Session 30mins, game 30mins |
This session is about full-backs and wingers stopping crosses into the penalty area.
Most attacks come from out wide, so the ability for defenders to be able to block crosses is essential, particularly in matches when our opponents have strikers who are good headers of the ball. This applies to most teams in our division.
At the end of each phase, we reset play, and rotate positions regularly.
What do I get the players to do?
Setting up as shown in the diagram, the server plays to the left-sided attacker (1). This player attempts to take on the winger or make room for a cross into a team mate who attacks the ball from his start position in the ‘D’.
1

In the second phase, we add an attacking full-back, plus an additional defender to create a 2v2 wing attack (2). The two defenders must stifle the threat of a cross.
2
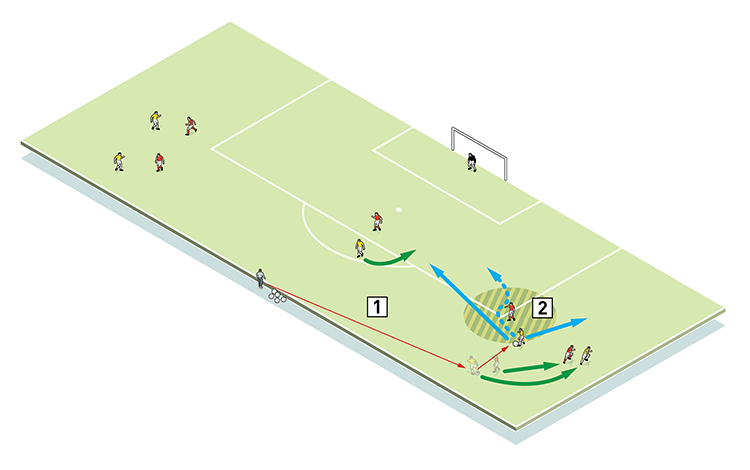
2. It is important for the defender to get his positioning right to hold up play and not ‘dive in
In the next stage, we progress again by going 8v8 and coning lines from the edges of the penalty area to the halfway line. Wingers and full-backs work outside this line (3), while midfielders must ensure a good supply of balls out wide, although the server can follow his pass to the wing to support.
3
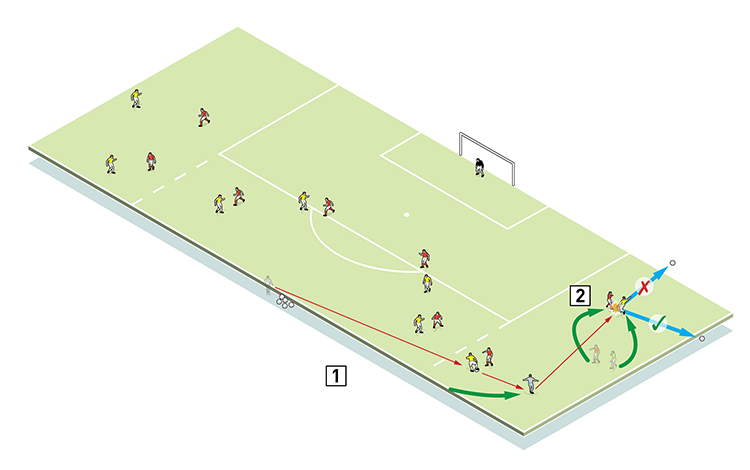
2. Good defensive angles from a tackle should result in a throw-in and not a corner
What are the key things to look for technically/tactically?
The role of the full-back is crucial - he must be alert to a number of attacking options, maintaining a position between winger and goal (4). Never diving in, he holds up the attacker to allow time for fellow defenders to support.
4
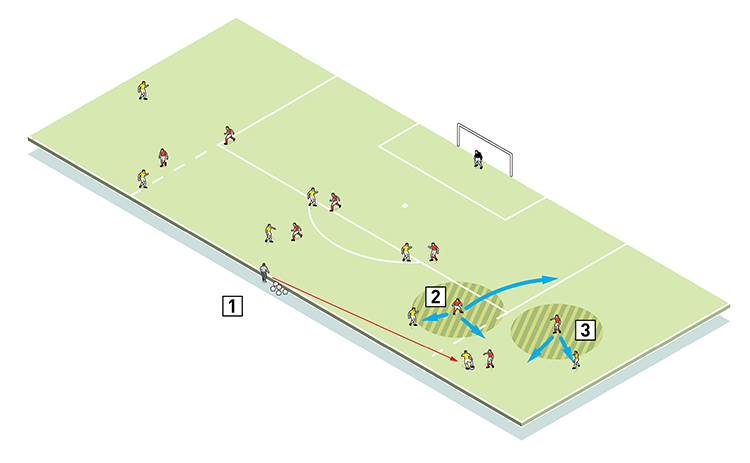
2. Defending midfielder should stay in contact with his attacker, but be ready to support the other defenders
3. Full back must cover the winger, but be ready to close down the attacker should he beat the first defender
We look at angles and distances between defender and attacker – the common fault is to be too tight or too far away. Angles vary depending on how far up the touchline the tackle is being made, but a defender should never be more than three yards away from the crosser. A defender at the wrong angle will fail to block the cross. If the ball is successfully blocked but goes out for a corner, the defender’s angles are slightly wrong. But if the cross is stopped and goes out for a throw-in he is perfectly positioned.
Defenders must also consider if the winger is quick or tricky, and right- or left-footed. Does he want him to go inside or outside? And he must also be well balanced should the attacker change direction at any time - over-striding is a common mistake.
How do I put this into a game situation?
In the set-up shown, the pitch is 50 yards long (5). Midfielders are two-touch, while wingers are conditioned to play in one half before, on the coach’s instruction, being allowed into the other half (1v1s leading into 2v2s). We can now drop in other individual training plans, such as defensive midfielders tracking in relation to full-backs (6).
5
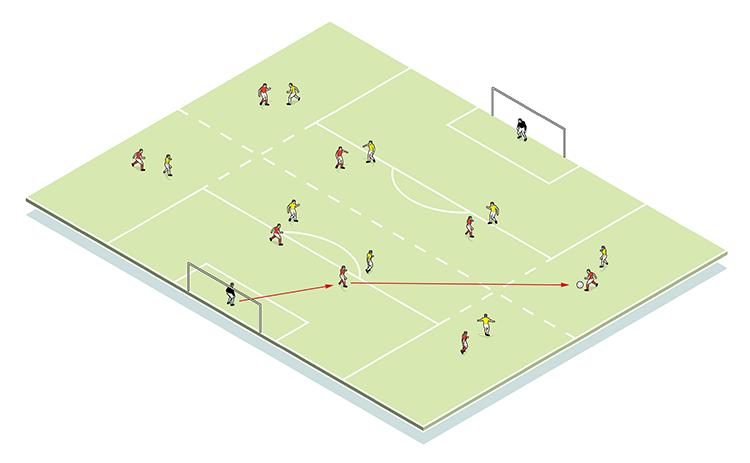
6

2. ... but when that condition is dropped, the defensive midfielder must track back to defend in relation to his full-back and centre-back
Related Files
Editor's Picks
Intensive boxes drill with goals
Penetrating the final third
Creating and finishing
My philosophy
Pressing initiation
Compact team movement
Defensive organisation
Back three tactics
Counter-pressing as an offensive weapon
Coaches' Testimonials

Alan Pardew

Arsène Wenger

Brendan Rodgers

Carlos Carvalhal

José Mourinho

Jürgen Klopp

Pep Guardiola

Roy Hodgson

Sir Alex Ferguson

Steven Gerrard
Related
Sunflower positioning
Out of possession match preparation
Coaches' Testimonials

Gerald Kearney, Downtown Las Vegas Soccer Club

Paul Butler, Florida, USA

Rick Shields, Springboro, USA

Tony Green, Pierrefonds Titans, Quebec, Canada
Join the world's leading coaches and managers and discover for yourself one of the best kept secrets in coaching. No other training tool on the planet is written or read by the calibre of names you’ll find in Elite Soccer.
In a recent survey 92% of subscribers said Elite Soccer makes them more confident, 89% said it makes them a more effective coach and 91% said it makes them more inspired.
Get Monthly Inspiration
All the latest techniques and approaches
Since 2010 Elite Soccer has given subscribers exclusive insight into the training ground practices of the world’s best coaches. Published in partnership with the League Managers Association we have unparalleled access to the leading lights in the English leagues, as well as a host of international managers.
Elite Soccer exclusively features sessions written by the coaches themselves. There are no observed sessions and no sessions “in the style of”, just first-hand advice delivered direct to you from the coach.








